Hardware-based security processing
Using a hardware-based high-speed, low-latency packet processing engine results in virtually no processing-induced latency. It enables packet forwarding, packet rewriting, encapsulation/decapsulation, encryption/decryption, load balancing, and more.
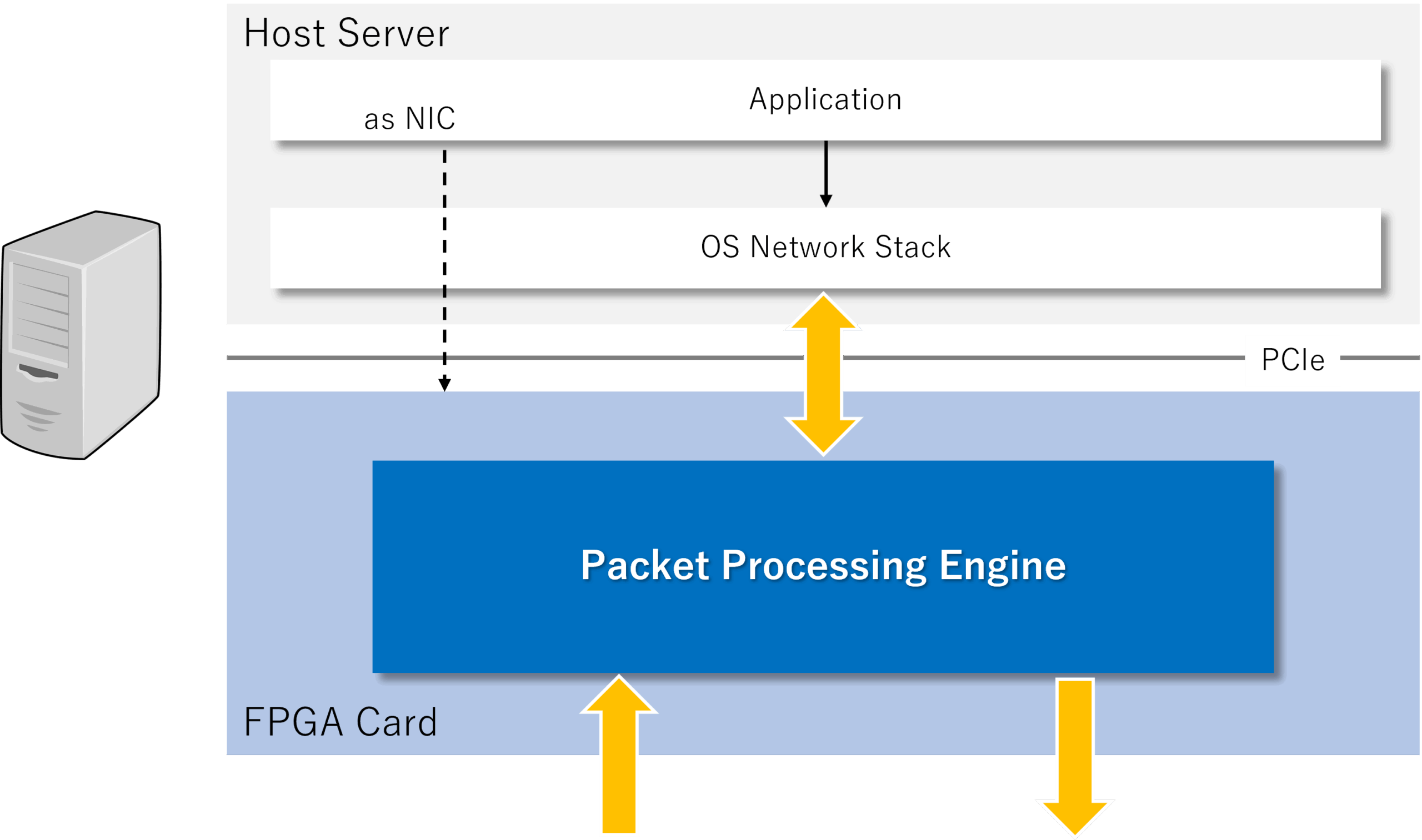
Offload packet processing from the server
Insert an FPGA card with a high-speed Ethernet interface into the server to offload the processing of incoming and outgoing packets using custom logic.
It supports diverse packet processing according to requirements, including security filters using DDoS filters, IP filters, protocol filters, and DPI (Deep Packet Inspection), as well as protocol conversion, transcoding, and encapsulation. Each engine can achieve a throughput of 100Gbps. Furthermore, since it can be treated as a NIC from the host application, it enables integration between conventional applications and the FPGA’s high-speed packet processing.
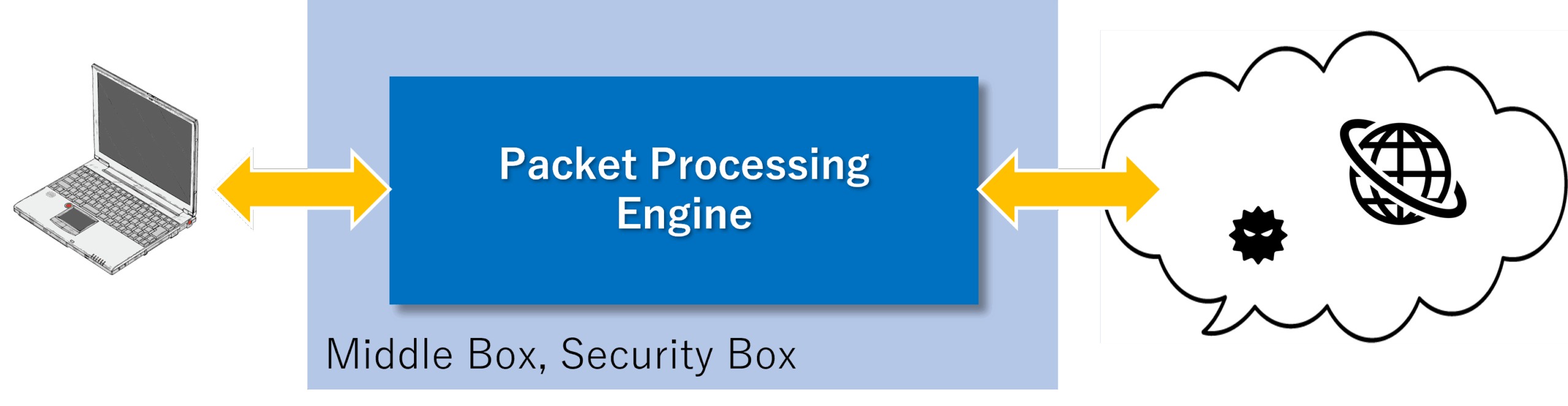
Middle-box / Security-Box
By offloading packet processing to hardware in the form of a middlebox outside the terminal, we prevent performance degradation and resource depletion without increasing the software processing load on the terminal.
Furthermore, due to the inherent characteristics of hardware processing, it can neutralize many attacks targeting memory resources and vulnerabilities that are problematic in software network stacks, thereby enhancing security.
Cryptographic System Development
By integrating the cryptographic engine with network protocols, we achieve an ultra-low-latency encrypted communication system. Furthermore, by integrating video input/output with the cryptographic engine, we realize a high-throughput, low-latency secure system.
High-Performance Cryptographic Implementation
Implementation techniques for highly parallel computation algorithms achievable only through hardware logic enable high throughput through parallelization even for dependent operations like counter modes and CRC.
Module Interlocking
PCIe integration, DMA, and coherent technology enable ultra-low latency by linking cryptographic hardware with network protocols, video I/O, and software.
Algorithm Examples
| Symmetric-key cryptography | – AES (128Gbps) – AES-GCM (128Gbps) – Chacha20 (128Gbps) – ChaCha20-Poly1305 (128Gbps) etc. |
| Public-key cryptography | – RSA – ECDHE (Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman Ephemeral) – PQC (ML-KEM, ML-DSA, SLH-DSA) etc. |
| Hash function | – SHA-2 (SHA-256, SHA-384) – SHA-3 |
