TCP/UDP Offload Engine
Our full-hardware TCP/UDP protocol stack enables CPU-free TCP/UDP communication. Despite being fully hardware-based, it supports over 10,000 simultaneous session connections and, with highly reliable retransmission control, can completely replace software-based TCP/UDP communication.
High performance and Low Latency
100 Gbps throughput per session (at 250 MHz operation)
Less than 1 microsecond delay
Over 10,000 concurrent sessions
High reliability
TCP ensures delivery through features such as timer-based retransmission, fast-retransmission and window probes. Furthermore, its high reassembly capability and flow control adapted to network conditions enable efficient transmission in any environment.
software compatibility
For socket library compatibility, applications that were previously processed by existing software will run without any changes whatsoever.
Linux, Zephyr, RTOS supported
Various API
- For user logic on FPGA, it provides a direct command and data stream interface without CPU.
- For SoC applications, data is placed in memory shared with the CPU, and TCP transmission and reception is achieved by kicking the TCP/UDP offload engine.
- For descriptors, it primarily transmits and receives data placed in host memory via PCI-express using TCP/UDP, with transfer control managed by descriptors that specify commands and data addresses.
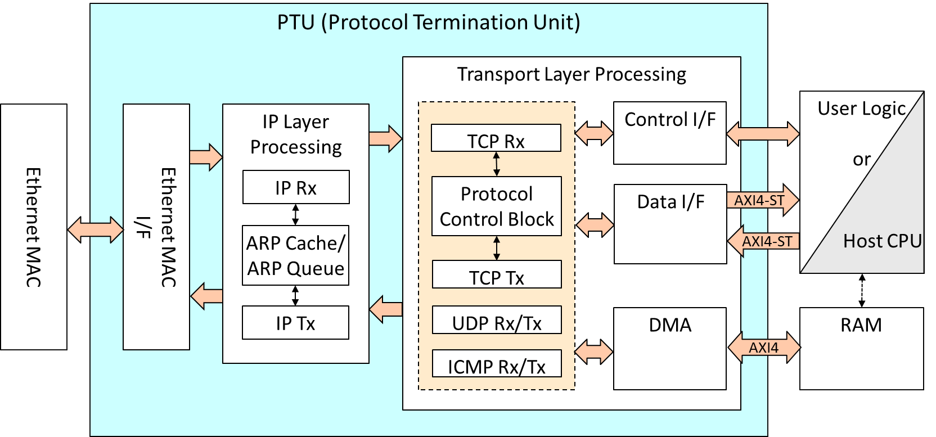
Hardware protocol stack
The TCP/UDP transport layer protocols, including lower-layer protocols such as IP, ARP, and ICMP, are offloaded from the CPU.
The TCP/UDP offload engine implements all functions—including ARP processing, TCP retransmission, TCP reassembly, and flow control—in hardware. The descriptor version enables zero-copy operations similar to RDMA by performing direct reads and writes from host memory, reducing CPU load to nearly zero.

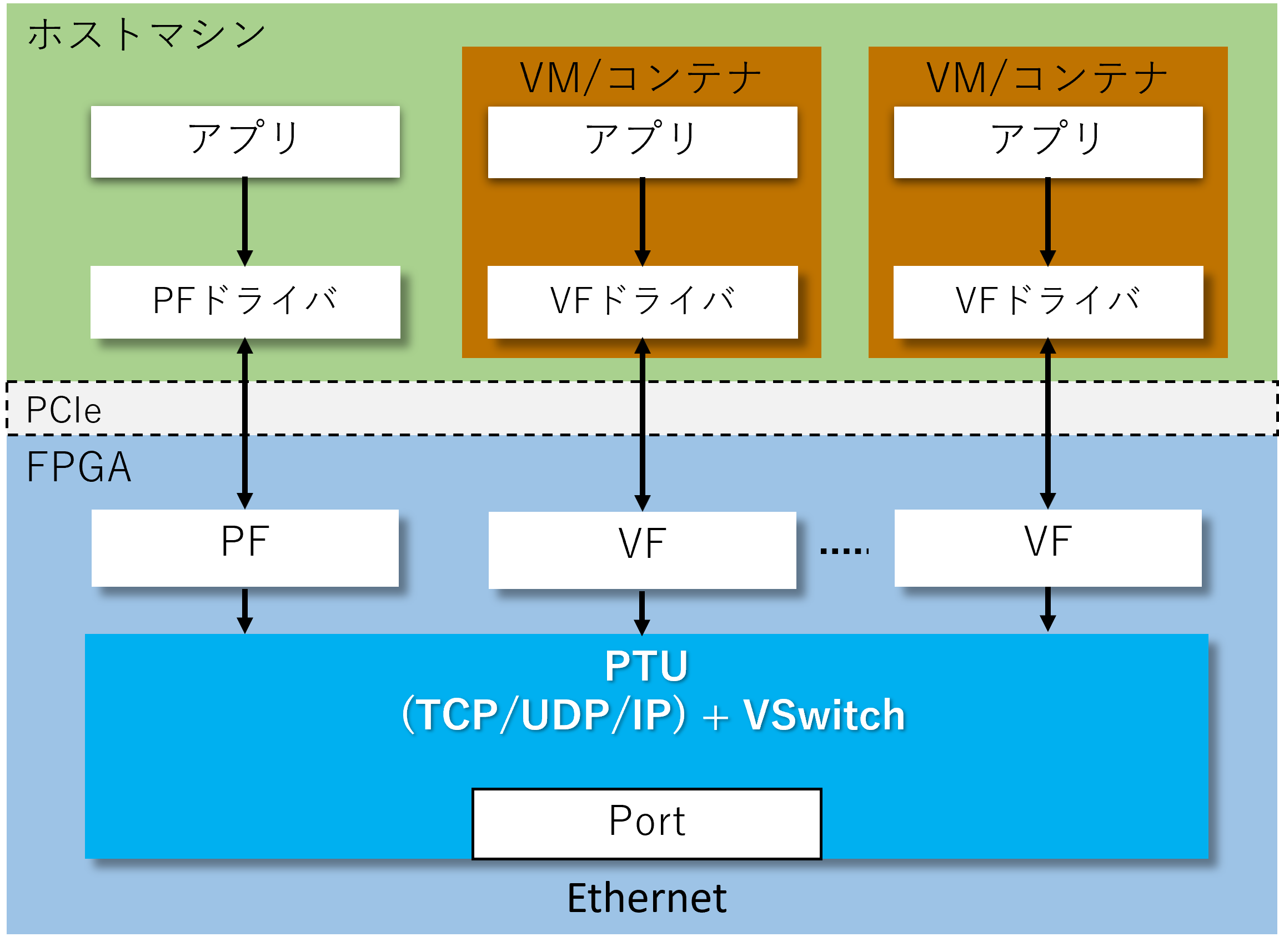
PCIe connectivity & virtualization support
The type controlled via descriptors can offload TCP/UDP processing on an FPGA connected via PCI-Express. This engine also supports SR-IOV (Single-Root I/O Virtualization). The hardware mediates and distributes requests from multiple virtual machines, enabling the offload engine to perform at full capacity without software overhead. Furthermore, it offloads packet switching functions between virtual machines—typically handled by hypervisor software—further reducing CPU load.
IoT Device Usage
AMD ZCU102 is an evaluation board for a System-on-Chip (SoC) type FPGA device, featuring an ARM CPU integrated into the FPGA.
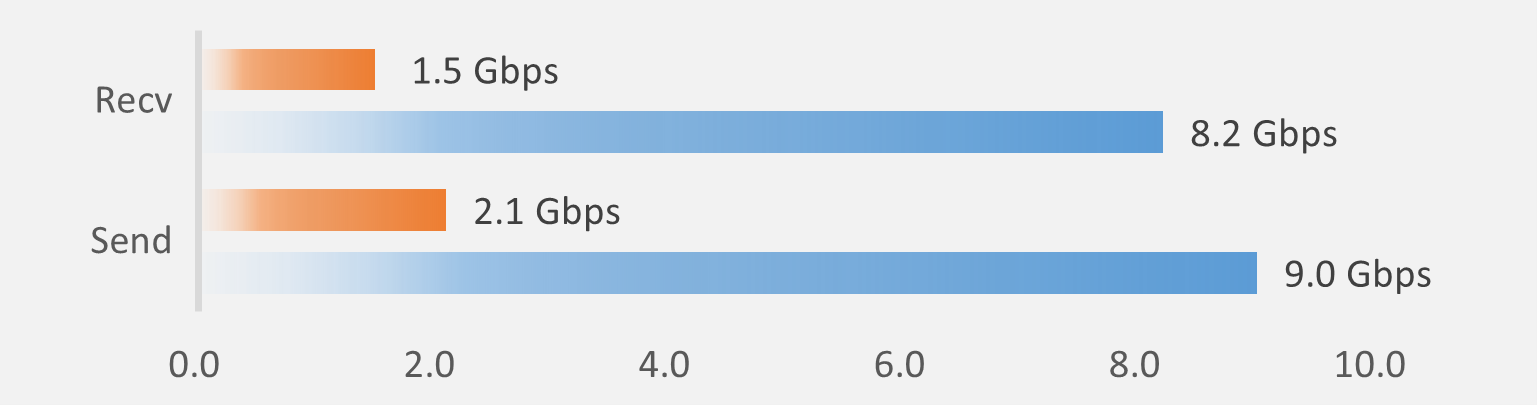
“iperf” is a tool that measures TCP transmission and reception performance, enabling comparison between scenarios with and without a TCP Offload Engine (ToE). When measuring with the ARM CPU, throughput is 2.1Gbps transmit and 1.5Gbps receive. However, by enabling ToE, throughput reaches 9.0Gbps transmit and 8.2Gbps receive without CPU load.
Major Specifications
| Protocol | 802.3, ARP, ICMP, IPv4, TCP, UDP, RTP |
| Throughput | 100Gbps (per one core, at 250MHz operation clock) |
| TCP | Functions: Packet generation, Checksum, 3-way handshake, Packet retransmission, High-speed retransmission, Flow control, TCP reassembly, Delayed Ack (Full TCP functionality equivalent to socket libraries) Maximum Connections: 16,000 (Configurable) TCP Options: Supports MSS (Maximum Segment Size), Supports TimeStamp |
| UDP | Over 10,000 sessions Upper Layer:GigE-Vision, H.264 over RTP Custom support for various protocols |
| Target devices | Altera: Arria/Stratix 4/5/10, Agilex, etc. Supports OFS (Open FPGA Stack) AMD: 7, UltraScale, UltraScale+, Versal, Alveo series Supports HBM, HBM2 Supports ASIC |
| Software I/F | Provided Linux driver supports socket library compatibility Supports Virtual Machines and Containers (has SR-IOV features) |
We have evaluation licenses and research licenses, please contact us.
